Table Of Content
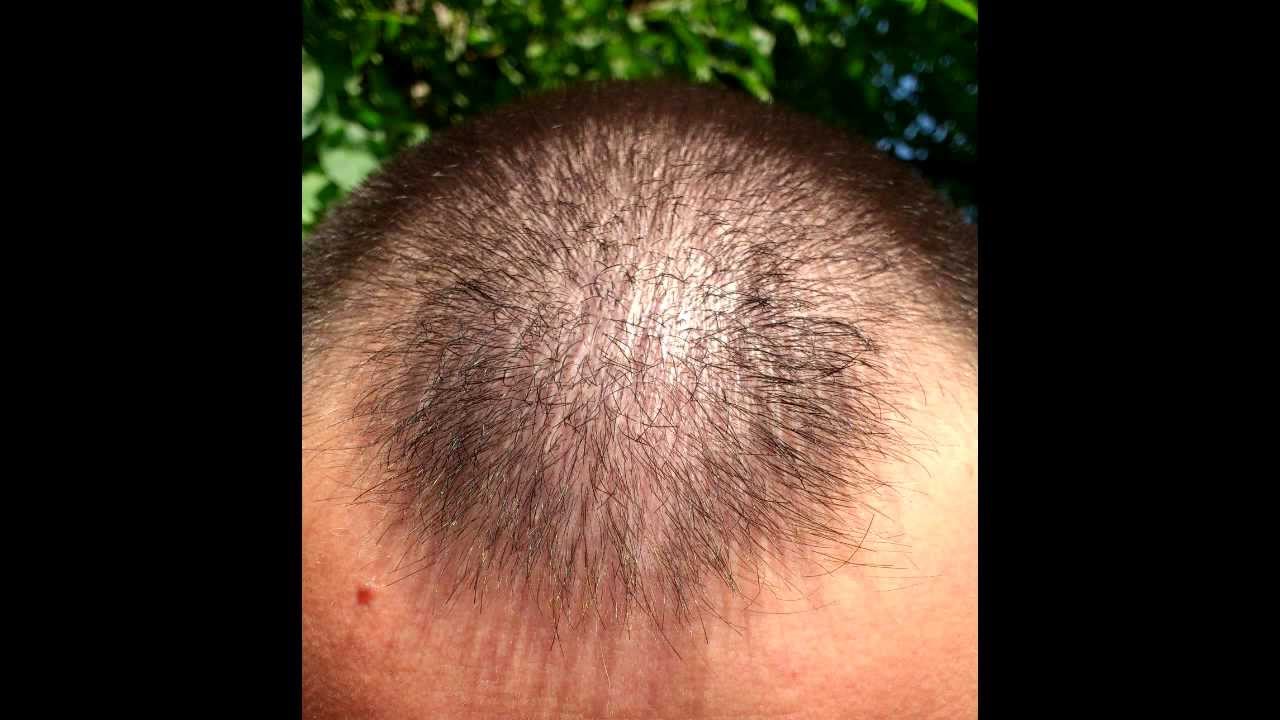
Also, when you start using minoxidil, you might notice more hair growth initially, followed by some shedding of old hair after two to eight weeks. This shedding is generally a sign that the treatment is working. Some studies and case reports suggest Rogaine’s potential benefit to hair growth of the eyebrows, beard, and facial hair. The medication's effectiveness is also unclear for certain kinds of alopecia, such as scarring alopecia. Men’s Rogaine was approved for hair loss based on its application only to the vertex of the head.
What may interact with this medication?

To understand how Rogaine works, understanding the basics of hair growth helps. Keep reading to learn more about how Rogaine works, what results to expect, and potential side effects. The findings from a recent study also suggest that menstruating younger, especially at age 10 or less, may increase stroke risk. Middle-aged women consuming plant-rich diets are less likely to develop chronic diseases, according to a new study. Depression increases the risk of heart disease, and heart disease increases the risk of depression — but possibly due to hormonal differences, women face...
NSW Waratahs trounce Drua to claim fifth Super Rugby Women's title
Minoxidil is also available by prescription as an oral tablet. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat high blood pressure. In some cases, healthcare providers prescribe oral minoxidil off-label for hair loss.
Medical Professionals
Minoxidil is also classed as a vasodilator, meaning that it dilates your blood vessels so that blood flows more easily where it’s applied. An increase in blood circulation to your scalp could be part of why minoxidil increases hair growth. Researchers observed that people who had alopecia and used minoxidil for hypertension experienced hair regrowth, and the world’s most popular over-the-counter treatment for alopecia was born.

"It is best used and most effective when the hair is thinning rather than completely lost," says Belmo. The route to getting best results is to work with a dermatologist who can help give a 360 approach to your hair loss causes and treatment. Appropriate studies have not been performed on the relationship of age to the effects of topical minoxidil in children. This is because minoxidil doesn’t cure the underlying cause of hair loss; it only treats the symptoms. If you stop treatment, the hair follicles will eventually return to their previous state, leading to renewed hair loss.
Who Should Not Use Rogaine?
Whilst minoxidil is approved for androgenetic alopecia (most common hair loss), it's not approved for all types of hair loss. "It cannot grow hair if the hair follicles are no longer present, these follicles can be lost in certain hair loss disorders known as scarring alopecias," explains Sharon Belmo. Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding shouldn’t use minoxidil, cautions the AAD, as traces of the drug can pass into breast milk.
Commonly, this condition is caused by genetics, hormones, and other health conditions. Because Rogaine is only FDA approved for hair growth at the vertex on top of the scalp, it’s not intended to treat receding hairlines. You may want to talk with your doctor about using it in other areas. Rogaine may cause some temporary hair loss for about 2 weeks.
14 Expert Tips to Make Your Hair Grow Faster in 2024 - Cosmopolitan
14 Expert Tips to Make Your Hair Grow Faster in 2024.
Posted: Wed, 13 Dec 2023 08:00:00 GMT [source]
It’s another expensive treatment that isn’t generally covered by insurance, but it tends to be a long-lasting solution. Finasteride (which goes by the brand name Propecia or Proscar) is another very popular topical hair loss treatment option. If you stop using Rogaine, any progress you make with your hair growth will revert back to where they would be without the medication.
Until the product takes full effect, you may notice that your hair initially grows back colorless and with a softer than normal texture. If you respond well to Rogaine, continued use should yield results that are the same color and thickness as the rest of your hair. DHT is one of the main causes of baldness in men because it binds to hair follicles and shrinks them.
However, the effectiveness is varied, at only a 30-40% success rate, which means that many people don’t respond to treatments. To know if Minoxidil will work for you, take the Minoxidil Response Test. One recent study showed that topical Minoxidil at any concentration had more positive results than the placebo. That same study also showed an additional 6.79 hairs/cm2 in the 5% concentration of Minoxidil treatment versus the 2% treatment. Give your health care provider a list of all the medicines, herbs, non-prescription drugs, or dietary supplements you use.
In general, minoxidil comes in two strengths and can be used topically or orally. The FDA has approved the 2% formula to treat women’s hair loss, while men can use the 5% solution. Usually, this increase in hair fall is referred to as minoxidil shedding. A 2004 study showed that 5% topical minoxidil was superior compared with 2% topical minoxidil. The study also found that the participants who used the 5% topical minoxidil had improved “psychosocial perceptions” of hair loss.
By contrast, scarring alopecia, another autoimmune disease that causes hair loss, is often accompanied by itchiness, tenderness and scaling of the scalp. Scarring alopecia is the most devastating type of hair loss, Mirmirani says, because it permanently destroys the hair follicles. The most common cause of alopecia is an inherited condition called male- or female-pattern hair loss. Unlike minoxidil, which does not target the hormones in your body, Finasteride works by preventing testosterone from being converted into DHT in the prostate, hair follicles and glands.
Rogaine is FDA approved to help with male and female pattern baldness. While it’s not FDA approved for other types of hair loss, your doctor may recommend it for off-label use. In addition to Rogaine, other medications are available that might help regrow hair. One is Propecia (finasteride), an oral tablet the FDA has approved for male-pattern baldness.


No comments:
Post a Comment